life cycle of a seedless plant
The sporophyte is the defining characteristic of the group. Non-vascular seedless plants include mosses hornworts and liverworts.

Plants Ii Non Vascular And Seedless Vascular Plants Biol110f2012 Confluence Vascular Plant Vascular Plants
The three groups lycophytes sphenophytes and pterophytes of seedless plants.

. The diploid sporophyte is the dominant phase of the life cycle while the gametophyte is an inconspicuous but still-independent organism. But inside every seed there is a tiny baby plant known as an embryo. One gametophyte produces sperm cells that fertilize the egg cells of another gametophyte forming a zygote.
The dominant phase of the life cycle of hornworts is the short blue-green gametophyte. Seedless plants produce spores instead of seeds and they can be vascular meaning they retain water in the tissue of the plant or they can be non-vascular. First week only 499.
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants alternates between a diploid sporophyte and a haploid gametophyte phase. Live worksheets English Science Plant reproduction Life cycle of seedless plant. The life cycle pattern in both Pteridophyta and.
Pteridophytes ferns are the seedless vascular plants. Seedless plants like these horsetails Equisetum sp thrive in damp shaded environments under the tree canopy where dryness is a rare occurrence. Enroll Today Dive Deep into the World of Biology.
Click here to view We have moved all content for this concept to for better organization. When spore land they grow into gametophytes. They have an alternation of generations not unlike the bryophytes the seedless nonvascular plants.
In the life cycle of a fern the sporophyte generation is dominant. Seedless plants like these horsetails Equisetum sp thrive in damp shaded environments under the tree canopy where dryness is a rare occurrence. Some protists also have an alternation of generations life cycle but the structures that produce gametes in protists are usually single cells.
The plant life cycle alternates between haploid and diploid generations. The sporophyte is the dominant stage of the plant which may be between a few millimeters. Seedless vascular plants have a dominant sporophyte stage in their.
The difference between seed plants and seedless plants is that seedless plants do not bear seeds for propagation whereas seed plants bear seeds for multiplication. They have a similar life cycle to that of seed-bearing plants. The life cycle pattern in both Pteridophyta and Spermatophyta is basically same.
The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants. The gametophyte is now less conspicuous but still independent of the sporophyte.
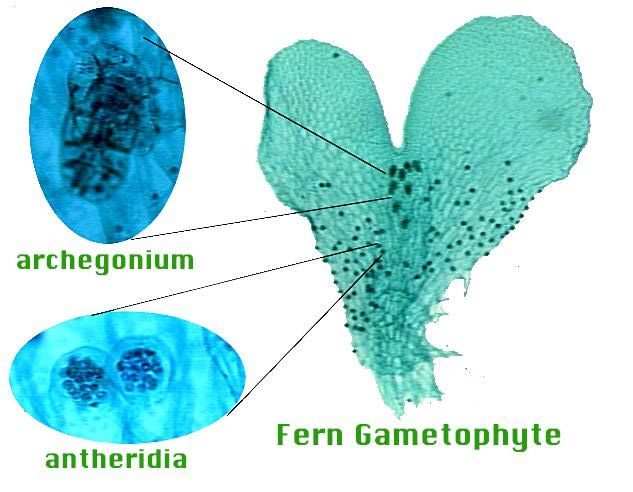
Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. From the outside seeds are protected by a tough layer called Outer Coat. This gametophyte contains the antheridia male sex organ and the archegonia female sex organ together on one plant.
Plants produce gametes in multicullar structures that have an outer protective layer. For a plants life cycle the diploid sporophyte is the most prominent while the gametophyte is a less noticeable but autonomous organism. Seedless vascular plants reproduce through unicellular haploid.
The sporophyte is the defining characteristic of the group. Plants in both divisions exhibit alternation of generations. Describes the life cycles of seedless vascular plants.
See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading. Sperm are produced in structures called antheridia. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants is an alternation of generations where the diploid sporophyte alternates with the haploid gametophyte phase.
The dominant phase of the life cycle of hornworts is the short blue-green gametophyte. Throughout plant evolution there is a clear reversal. The life cycle of seedless vascular plants shows an Alternation of Generations.
Seeds wait to germinate until three needs are met- water correct. Both the diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte are independent of each other in the seedless vascular plant. During the life cycle of a seedless plant sporophyte releases.
The dominant phase of the life cycle of hornworts is the short blue-green gametophyte. The sporophyte is the defining characteristic of the group. Life cycle of seedless plantLife cycle of moss and fern.
The lightweight spores allow. The plant life cycle starts with a seed. Life cycle of seedless plantLife cycle of moss and fern.
It is a long and narrow pipe-like structure that emerges from the parent gametophyte and maintains growth. The diploid sporophyte however is the more prevalent noticeable generation. The life cycle of plants can be broken into 5 main stages which are.
Describe the adaptations in members of this group that allow them to be successful in terrestrial environments. Non-vascular plants require water to thrive because they dont have the means to retain water on their own. The seedless vascular plants go through an alternation of generations just as the nonvascular plants and other vascular plants do.
We have a new and improved read on this topic. This then grows into a sporophyte. First the sporangium releases many spores formed by meiosis which germinate in moist soil to form a haploid gametophyte.
During the seedless vascular plants life cycle there occurs an alternation of plant evolution in which the diploid sporophyte alternates. The haploid plant that produces gametes is called a gametophyte. Identify the characteristics of non-vascular plants.
Describes the life cycle of seedless vascular plants. Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. The embryo has a root shoot as well as the first true leaves.
After that further growth starts and the plants reaches maturity where it pollinates and gives seeds so that its species continue to survive by starting the life cycle again. About sporophyte stage of seedless plant. The dominant part of the fern life cycle is the diploid sporophyte generation -.
Water serves as a means to disperse spores away from the parent sperm swim through the water to fertilize the female egg. We have a new and improved read on this topic. Compare and contrast the life cycle of a seedless vascular plant and a seed plant This problem has been solved.
Ad Comprehensive Biology Course.

Fern Plants And Their Life Cycle Seedless Vascular Updated Plants Fern Plant Vascular Plant

Classifications Of Flowering And Non Flowering Plants Plant Classification Biology Plants Teaching Plants

List Of Seedless Vascular Plants Planting Shrubs Plants Septic Mound Landscaping

The Surprising Way Ferns Reproduce Fern Life Cycle Ferns Plants

Life Cycle Of The Fern Candace Jordan Class Plant Life Cycle Ferns Fern Life Cycle

Moss Life Cycle Life Cycles Biology Plants Biology Projects

Types Of Plants Classifying Plants Types Of Plants Plants

Https Session Masteringbiology Com Myct Itemview Offset Next Meiosis Mitosis Egg Forms

Lab Ch 16 Non Vascular Plants And Seedless Vascular Plants Biology 152 With Kinnes At Azusa Pacific University Studyblue Vascular Plant Plants Vascular
Page Not Found Uroki Biologii Biologiya Botanika

Ferns An Ecological Manual Of New York City Plants In Natural Areas Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles Ferns

Department Of Botany Botany Biology Plants

Western Sword Fern Life Cycle C Don Boucher Vegetal Biologia Plantas Jardin

Related Image Life Cycles Fern Life Cycle Life Cycle Stages

4 Gb2 Learnres Web 06plan Plants Vascular Plant Gymnosperm

Bryophyta Moss Life Cycle Life Cycles Biology Plants Biology Projects

Fern Life Cycle Plant Life Cycle Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles

Pin By Dandavats Dasa Flores On Botany Fern Life Cycle Life Cycles Rhizome
